Every classroom, training hall, or family study corner shares one truth: no two learners are alike. Teachers often struggle to adapt lessons for mixed-ability classes and begin asking what are learner differences that make each student unique. Parents, too, wonder why siblings learn so differently. The OECD reports that over 60% of teachers identify learner diversity as their biggest daily challenge. Psychology backs this up, a research from Howard Gardner on multiple intelligences shows that people process knowledge in unique ways. As Dr. John Hattie, a leading voice in education, puts it, “recognizing individual differences is the first step toward real impact.”
In short, when we ask what are learner differences, the answer is clear: they aren’t a problem to fix, they’re the core reality of modern education. Understanding them helps schools close gaps, parents support growth, trainers boost engagement, and EdTech build smarter tools.
Explore More:
Instant Answer
Learner differences are the measurable variations in how students and adults absorb, process, and apply knowledge, shaped by cognitive, cultural, emotional, and motivational factors. They explain why two learners can sit in the same class yet perform very differently. Teachers address learner diversity with strategies like differentiated instruction, inclusive methods, and adaptive learning systems.
Why Do Students Learn Differently?
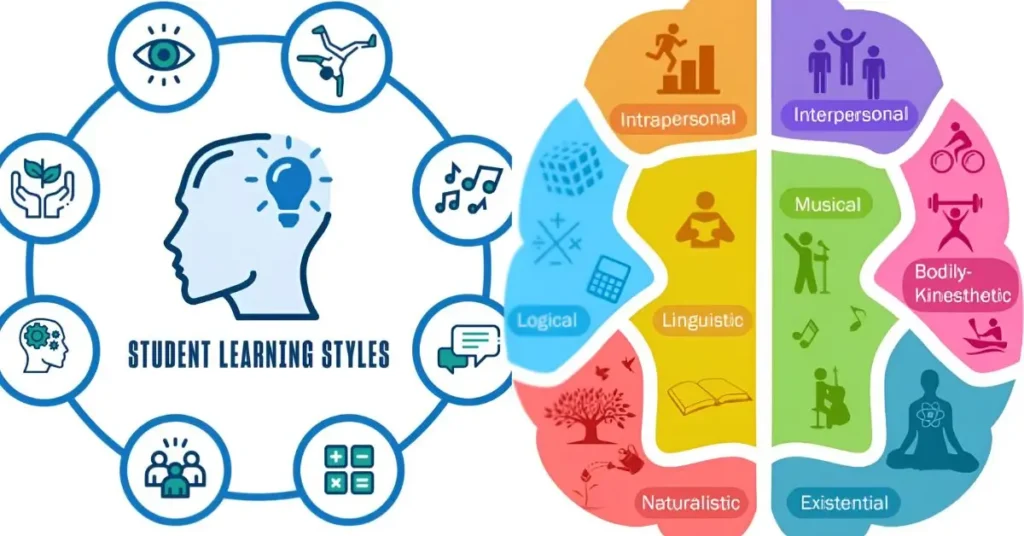
Students learn differently because of cognitive differences, prior knowledge, culture, motivation, and even learning environment. Some grasp abstract math quickly, while others need concrete visuals. For parents, this explains why homework battles vary between kids. For trainers, it’s why one employee loves role-play exercises, while another prefers reading guides.
Key factors include:
- Cognitive abilities (memory, attention, reasoning)
- Learning styles (visual, auditory, kinesthetic)
- Cultural background (values, communication norms)
- Motivation and mindset
- Support systems at home or work
Key Intake: Learner differences exist because brains, experiences, and motivations aren’t uniform.
How Can Teachers Address Learner Differences?
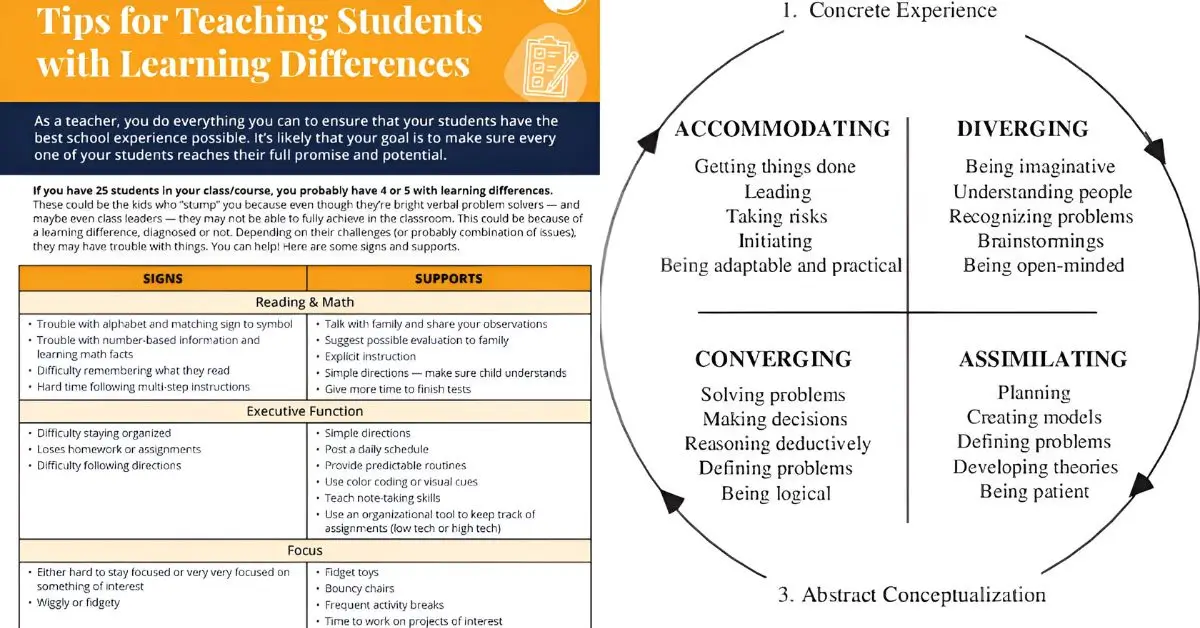
Teachers handle learner diversity through differentiated instruction and inclusive teaching strategies. This means planning lessons with multiple entry points so fast and slow learners both engage.
Practical methods:
- Use choice boards (students pick task formats).
- Mix group work + solo tasks.
- Scaffold lessons with tiered levels of difficulty.
- Apply formative assessment to adjust on the fly.
Example: In a mixed reading class, one group might analyze the theme, while another works on vocabulary. Both feel challenged without being left behind.
What Factors Influence Learner Differences Most?
Several forces shape learner diversity, but research highlights three strongest drivers:
- Cognitive development (IQ, processing speed).
- Motivation and engagement (intrinsic vs. extrinsic).
- Cultural and socio-economic context.
For leaders, this means addressing achievement gaps isn’t just about curriculum it’s about equity. For EdTech designers, it signals the need for adaptive learning systems that adjust in real time.
What Is an Example of Learner Differences?
A clear example is math learning styles:
- Student A solves equations in their head.
- Student B needs visual step-by-step diagrams.
- Student C learns best by teaching the concept to peers.
Each approach reflects individual differences in learning, proving there’s no single “best method.”
How Do Cultural Backgrounds Affect Learner Differences?
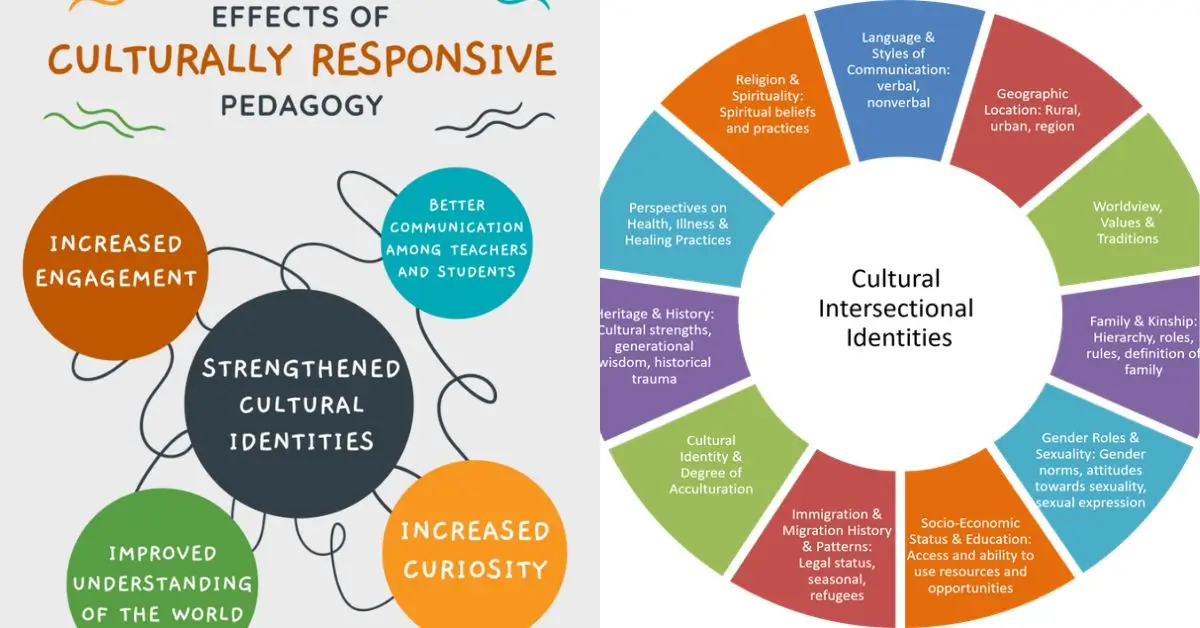
Culture shapes how students interpret knowledge. In some cultures, group learning is valued, while others push independent problem-solving. Corporate trainers face this when global teams resist one-size-fits-all programs.
Fact: UNESCO research shows cultural context directly affects student engagement factors like participation, confidence, and motivation.
What Role Does Motivation Play in Learner Differences?
Motivation can accelerate or block learning outcomes. A disengaged but capable learner often underperforms compared to a motivated peer with fewer natural abilities. Parents see this when a child breezes through gaming tutorials but drags through homework.
Tip for teachers: link content to real-world goals.
Tip for trainers: gamify tasks for adult learners.
Which Teaching Methods Help Diverse Learners?
Effective strategies balance personalized education with scalable practices.
- Differentiated instruction for classrooms.
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL) for inclusivity.
- Adaptive digital platforms for real-time support.
Corporate trainers can mirror this with modular workshops, while special education staff rely on multi-sensory instruction.
How Do Learner Differences Impact Classroom Success?
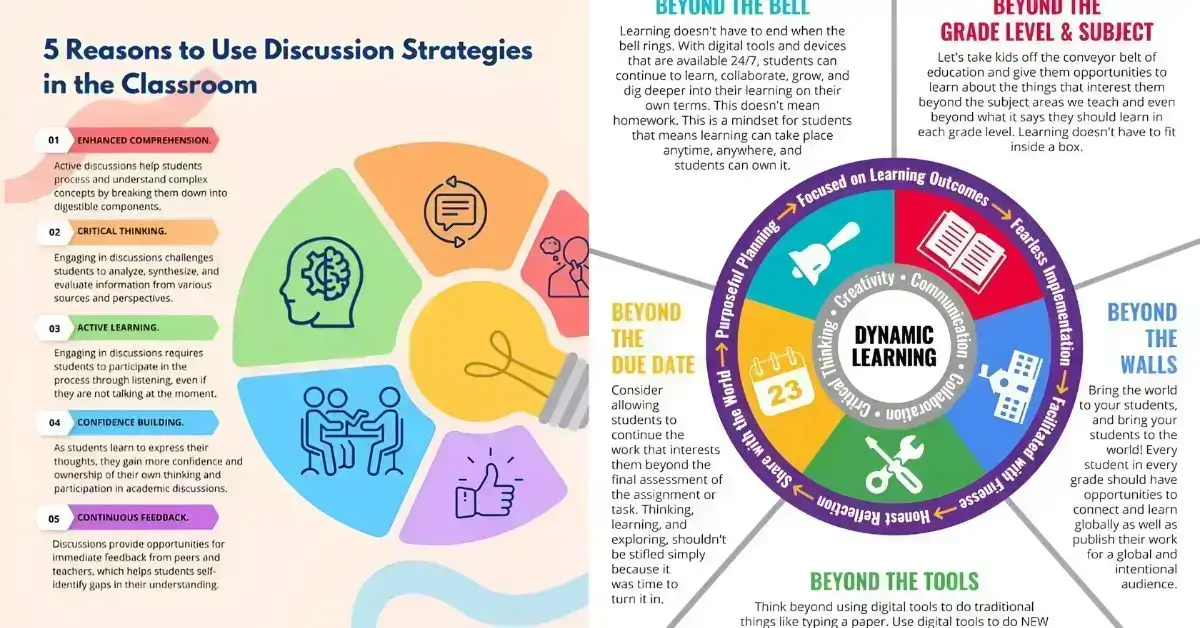
Classrooms with unchecked learner differences risk widening achievement gaps. But when teachers adapt, student engagement and academic performance improve across all groups.
School leaders should see learner diversity as a strategic lever: the way to raise both equity and results.
Which Theories Explain Learner Differences?
Several educational psychology theories explain what are learner differences and why they matter:
- Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences (different cognitive strengths).
- Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development (learning within reach with support).
- Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle (learners prefer different processing modes).
Education students often encounter these on exams, but for practice, they guide lesson design, special ed strategies, and EdTech frameworks.
Sources
- American Psychological Association (APA): Belief in learning styles myth may be detrimental (2019)
- OECD: Education at a Glance 2024: OECD Indicators
- University of Michigan: Roundup on Research: The Myth of ‘Learning Styles’
- Jacobs Foundation: Advancing Research on Learning Variability
- Edutopia: The 10 Most Significant Education Studies of 2024
FAQ’s
What are learner differences in education?
They are the unique ways students process and apply knowledge, shaped by cognitive, cultural, and motivational factors.
Why do students learn differently?
Brains, experiences, and environments vary so no two students learn the same way.
How can teachers address learner differences?
Through differentiated instruction, flexible grouping, and inclusive methods.
What factors influence learner differences?
Cognition, motivation, culture, prior knowledge, and socio-economic conditions.
What is the difference between learning styles and learner differences?
Learning styles are preferences; learner differences are broader and include abilities, culture, and motivation.
How can parents support learner differences at home?
By recognizing their child’s strengths, providing varied resources, and keeping expectations realistic.
Why are learner differences important in modern education?
They guide how schools, trainers, and EdTech adapt instruction for real impact.
Author Bio
Lena Moretti is an Educational Strategist with 12 years of experience in teaching and EdTech design, Lena specializes in bridging learner diversity with practical classroom and corporate training solutions.











