Slow internet, odd network spikes, or random pop-ups often trace back to one thing: what is DNS traffic. IT admins, business owners, and even home users deal with it daily without realizing it. According to Cisco Talos, over 90% of malware uses DNS traffic at some stage. Cloudflare reports that DNS handles trillions of requests per day, making it one of the most watched signals in cybersecurity. Yet, the truth is, most people don’t know what DNS traffic really means.
Explore More:
Instant Answer:
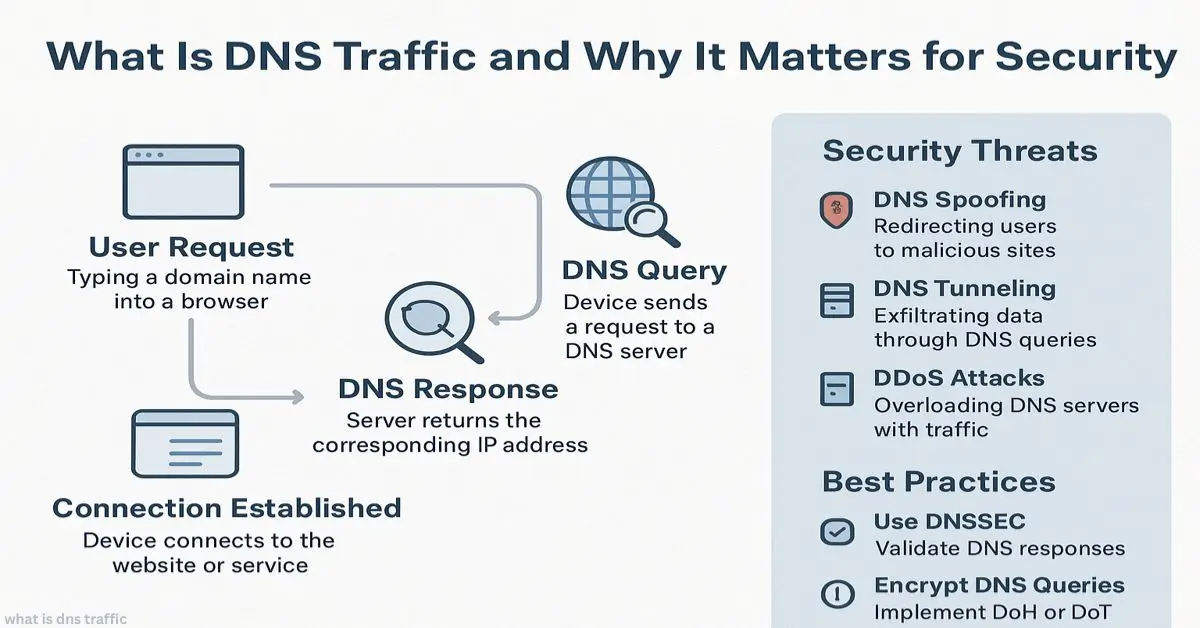
DNS traffic is the exchange of requests and responses between your device and DNS servers. Each time you enter a web address, your computer asks the DNS to translate it into an IP. Tracking this traffic helps detect slowdowns, threats, and unusual activity.
What Is DNS Traffic in Simple Terms?
What is DNS traffic in everyday language? It’s like a phonebook lookup happening behind the scenes. You enter google.com, and DNS finds the number (IP address) for you.
- Request: Your device asks the DNS server for an IP.
- Response: DNS replies with the address.
- Traffic: The packet exchange itself.
Think of it like a digital handshake. Without DNS traffic, the internet wouldn’t know where to send you.
How Does DNS Traffic Work?
DNS traffic works by breaking down every lookup into small packets.
- You type a website name.
- The request travels through your network.
- The DNS resolver finds the matching IP.
- The answer returns, letting your browser connect.
This process is fast, often milliseconds but across millions of users, the load creates noticeable patterns.
Why Is DNS Traffic Important?
DNS traffic matters because it’s both a performance metric and a security signal.
- Performance: Too many DNS lookups, slow apps and websites.
- Security: Odd DNS patterns often reveal malware or data theft.
- Visibility: Tracking DNS gives IT teams a map of network behavior.
Gartner has called DNS “the most overlooked layer in cybersecurity.”
What Causes High DNS Traffic?
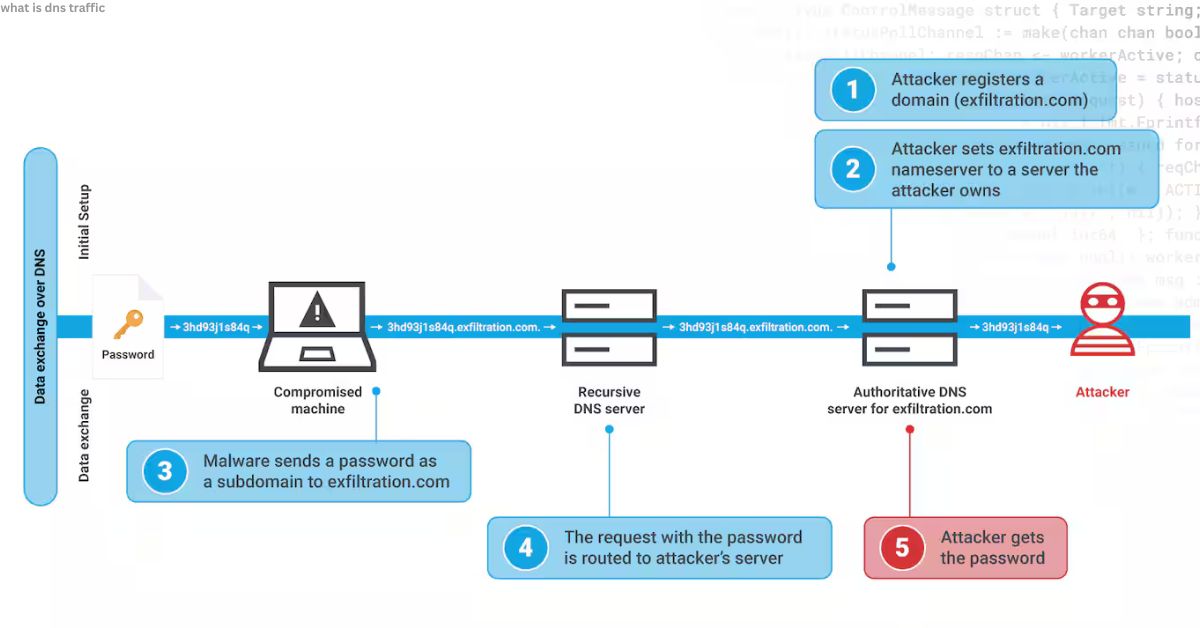
High DNS traffic happens when something generates too many lookups at once.
Common causes:
- Misconfigured apps or devices looping requests
- Malware contacting command-and-control servers
- DDoS (distributed denial of service) attacks
- Heavy user load (spikes during events or launches)
Key Intake: High DNS traffic isn’t always bad but unexplained spikes usually signal trouble.
How Does DNS Traffic Affect Internet Speed?
Every DNS lookup adds a small delay. Multiply that by dozens of resources on one webpage, and slowdowns add up.
- Normal: Milliseconds per request
- Problematic: Seconds per lookup → pages lag, apps hang
That’s why caching (storing recent DNS answers) is vital. It cuts repeated lookups and keeps browsing smooth.
DNS Traffic vs Web Traffic: What’s the Difference?
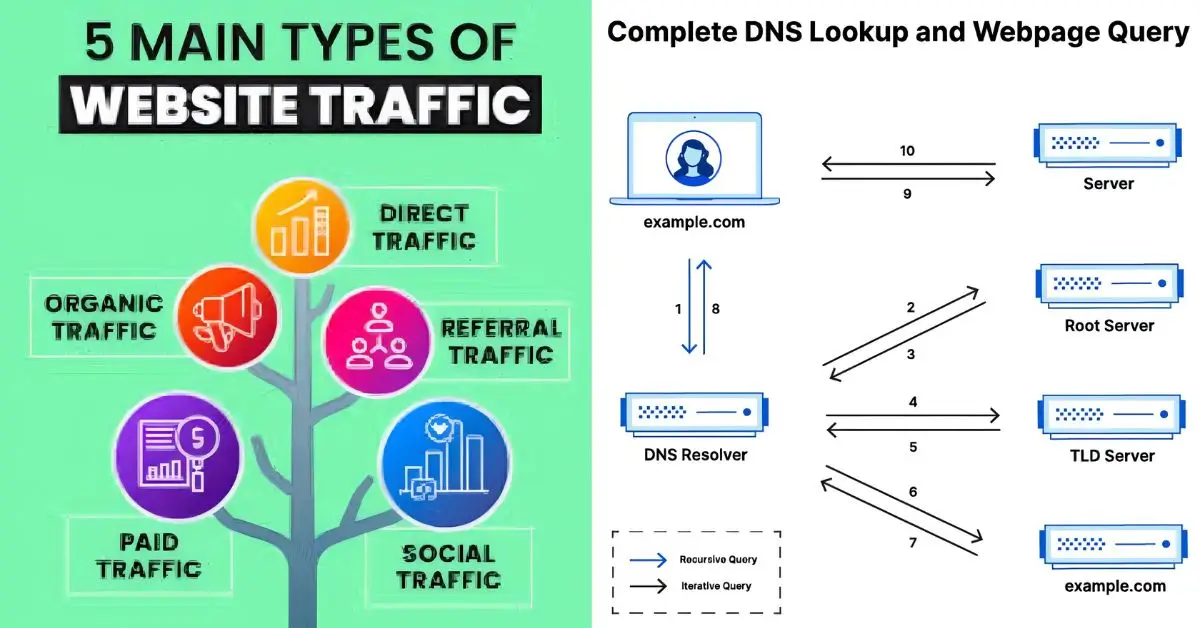
Many confuse DNS traffic with web traffic. They’re related but not the same.
- DNS traffic: Name-to-number lookups (small packets).
- Web traffic: Actual content transfer (videos, text, images).
Think of DNS as directions and web traffic as the actual trip.
How to Monitor DNS Traffic for Security
You can’t protect what you don’t watch. Monitoring what is DNS traffic reveals when something strange is happening.
Popular tools:
- Wireshark — packet-level inspection
- Cloudflare Radar — global DNS trends
- Cisco Umbrella — enterprise protection
- OpenDNS — home + business security
Monitoring answers key questions:
- Which domains are queried most?
- Are unknown servers contacted?
- Do patterns match known attack behaviors?
Which DNS Traffic Patterns Signal Attacks?
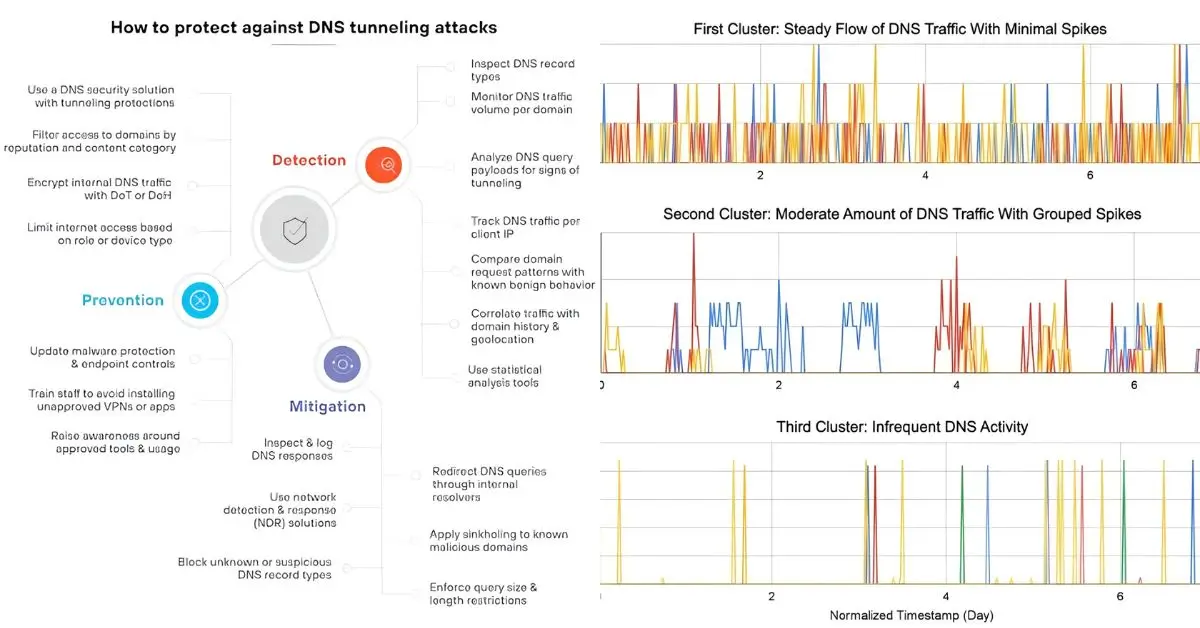
Certain DNS signals act like red flags:
- Unusual volume — too many lookups in seconds
- Odd domains — random strings or newly registered names
- Frequent NXDOMAIN errors — failed lookups from malware
- Regular beaconing — steady pings to suspicious server.
Ever wonder why ransomware often slips in unnoticed? It hides in DNS first.
Real-World Example: Malware in DNS Traffic
In my own testing, I saw a small business network where printers were generating thousands of DNS queries per minute. Turns out, malware was tunneling data through DNS. The fix? Blocking suspicious domains at the firewall.
Truth is, most people miss these signs because DNS is invisible until monitored.
Common DNS Traffic Issues and Fixes
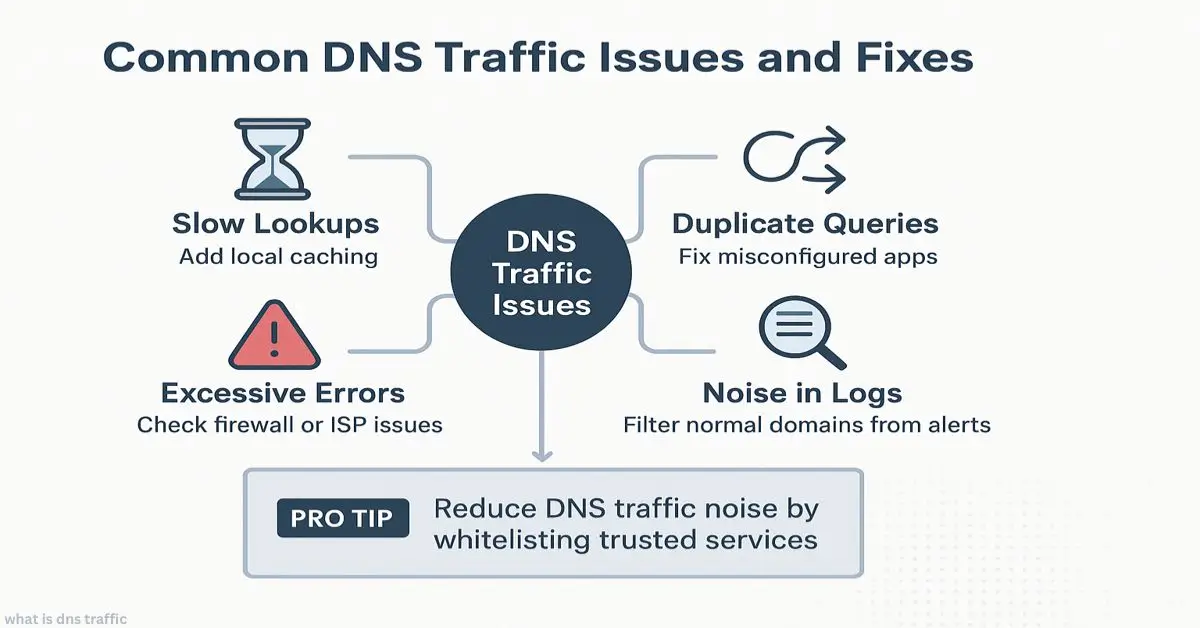
- Slow lookups → add local caching
- Duplicate queries → fix misconfigured apps
- Excessive errors → check firewall or ISP issues
- Noise in logs → filter normal domains from alerts
Pro tip: Reduce DNS traffic noise by whitelisting trusted services.
How to Log and Analyze DNS Traffic
Steps:
- Enable DNS logging in your server or router.
- Export logs to SIEM (Security Information and Event Management).
- Use visualization (graphs, dashboards) to spot spikes.
- Compare with known threat feeds.
Give it a shot you might be surprised at how much is hiding in plain sight.
Final Takeaway
DNS traffic is more than noise, it’s a lens into performance and security. IT admins spot anomalies, businesses protect uptime, and home users stay safe. Ignore it, and you miss slowdowns and attacks. At its core, what is DNS traffic isn’t just technical it’s practical. Understanding it helps cut outages, speed up fixes, and block threats, giving everyone clearer visibility into how the internet works.
Sources:
- Cloudflare: The evolving DNS threat landscape (Trusted industry leader in DNS security and performance)
- Cisco Talos: Widely cited research showing over 90% of malware leverages DNS traffic
- TechTarget: What is the Domain Name System (DNS)? (Authoritative reference for networking concepts)
- Wikipedia: Comprehensive overview of the Domain Name System and its history
- Akamai: In-depth analysis of DNS traffic management and global best practices
FAQ’s
What is DNS traffic in simple words?
It’s the back-and-forth of devices asking DNS servers to translate website names into IP addresses.
How does DNS traffic reveal malware?
Malware often sends odd or frequent DNS requests. These patterns stand out during monitoring.
Why monitor DNS traffic for cybersecurity?
Because most threats touch DNS first. Spotting anomalies early prevents larger breaches.
Which tools track DNS traffic best?
Wireshark, Cisco Umbrella, and Cloudflare are trusted tools for different needs.
How to reduce DNS traffic noise?
Cache results, fix misconfigured apps, and filter common trusted domains.
Author Bio
Daniel Mercer is a Cybersecurity Analyst with 12+ years in network monitoring and DNS threat detection. Writes practical guides for IT admins, SMBs, and security teams.