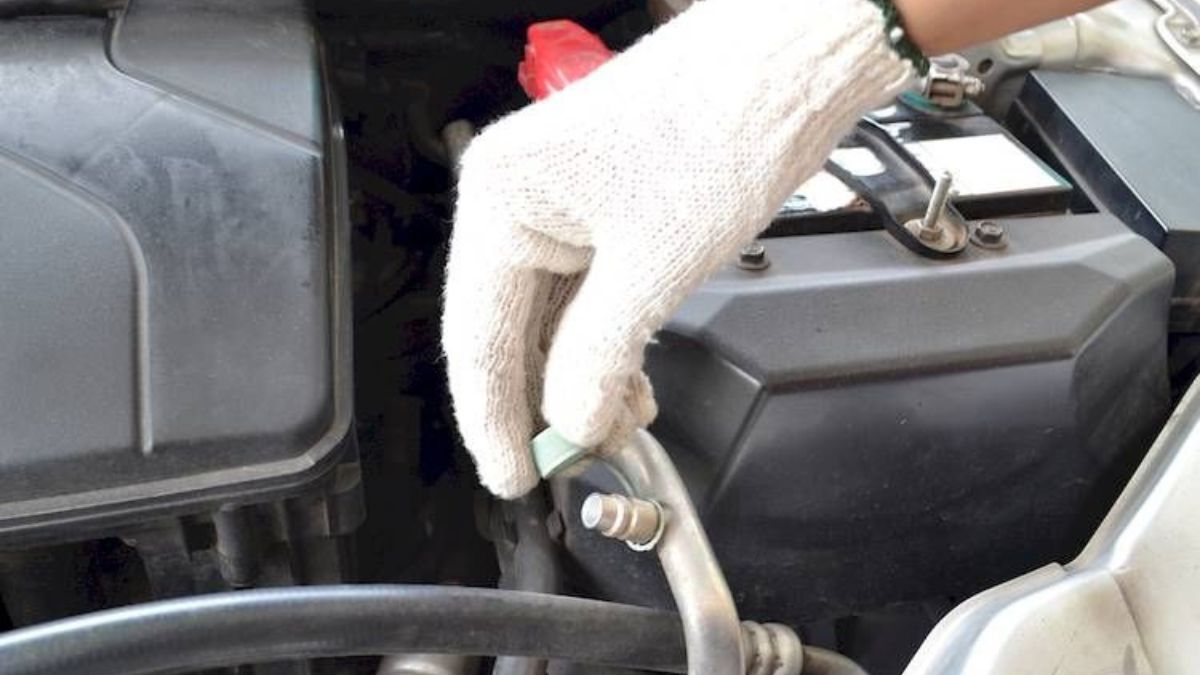
In any industrial system, valves are critical for controlling flow, maintaining pressure, and ensuring stability. When a valve fails, the consequences are often immediate and severe. Whether you manage a refinery, water treatment facility, or manufacturing plant, a single failure can lead to costly downtime, safety hazards, and environmental risks. For those managing industrial piping projects, prevention is essential. High-altitude pressure changes and freezing temperatures demand durable, well-maintained valves that can withstand diverse operational environments. Investing in the right components and regular maintenance is the only way to ensure consistent performance and system safety.
What Really Happens When a Valve Fails?
Valves are often overlooked but play a critical role in system operations. A malfunctioning valve can halt flow or allow uncontrolled flow, both of which are dangerous in high-pressure or hazardous environments.
Common outcomes of valve failure include:
- Uncontrolled Leaks: Leaking fluids or gases can lead to contamination, corrosion, or safety violations. In chemical plants, this can quickly escalate into a hazardous event.
- Pressure Build-up: If a valve fails to open, pressure can increase rapidly in certain parts of the system, risking pipe bursts or equipment damage.
- Product Loss: Faulty valves can lead to the loss of materials, affecting productivity and leading to financial waste.
- Equipment Failure: An underperforming valve can place excess strain on pumps, tanks, and connected systems, accelerating wear and reducing equipment life.
Common Causes of Valve Failure
Identifying the causes of valve failures is key to developing effective prevention strategies. In industrial environments, these are the most common reasons:
1. Corrosion and Rust
Harsh chemicals, moisture, and fluctuating temperatures contribute to material degradation over time. If the valve material isn’t resistant to the substances flowing through it, corrosion is inevitable.
2. Improper Sizing
When a valve is not sized correctly for the system’s flow or pressure requirements, it may operate under stress, leading to quicker failure. Oversized valves can also cycle too frequently, causing internal wear.
3. Mechanical Wear
With repeated opening and closing cycles, the internal mechanisms of a valve may wear down—especially in high-use systems. This is often seen in fast-moving manufacturing facilities or high-demand operations.
4. Installation Errors
Improper alignment, loose connections, or inadequate sealing during installation can compromise a valve’s long-term performance. Even the best valve will fail if not installed correctly.
5. Lack of Maintenance
Routine inspections and maintenance are often skipped until issues arise. Without regular lubrication, cleaning, and pressure testing, valves become more prone to failure.
How to Prevent Valve Failures in Industrial Systems
To avoid the consequences of valve failure, prevention must start from the very beginning—during the planning and installation phase—and continue throughout the valve’s operational life.
Select the Right Valve for the Job
Each system requires specific temperature, pressure, and media conditions. Choosing the right valve type—ball, gate, butterfly, or globe—is crucial. For industrial operations, selecting valves suited for extreme temperatures or high altitudes ensures reliability.
Ensure Proper Installation
A professional installation that includes alignment checks, torque settings, and correct sealing minimizes the risk of future issues. It’s also vital to verify compatibility with the piping system’s materials and flow direction.
Schedule Regular Maintenance
Establish a maintenance routine that includes:
- Visual inspections
- Checking for leaks or rust
- Testing operation under normal flow and pressure
- Replacing worn components like seals and gaskets
Proactive valve maintenance can prevent costly shutdowns and extend the life of the entire system.
Use Quality Control Measures
Strict quality assurance protocols—including pressure rating tests and response time checks—establish a performance baseline to monitor system health over time.
Why Industries Need Extra Attention
Industrial environments often face unique environmental and regulatory hurdles. Factors like freezing winters, mineral-heavy water, and high altitudes require precise valve selection and system design. To prevent premature failure, facilities must account for these local conditions when engineering their systems. Utilizing high-quality valve solutions and committing to regular inspections ensures efficiency and compliance—especially in critical regional sectors like mining, energy, and water treatment.
Conclusion
A single faulty valve can cause significant disruptions, but proper planning and regular maintenance can help mitigate these risks. Reliable performance begins with selecting the right industrial pipe valves for Utah environments, ensuring proper installation, and maintaining them consistently. A well-planned valve strategy safeguards your workforce, product, and bottom line, making it an essential step for any industrial operation focused on long-term success and system reliability.