Table of Contents
- Importance of Hands-On STEM Learning
- Successful Initiatives in Middle Schools
- Strategies for Implementing Hands-On STEM Activities
- Overcoming Challenges in STEM Education
- Future Trends in Middle School STEM Education
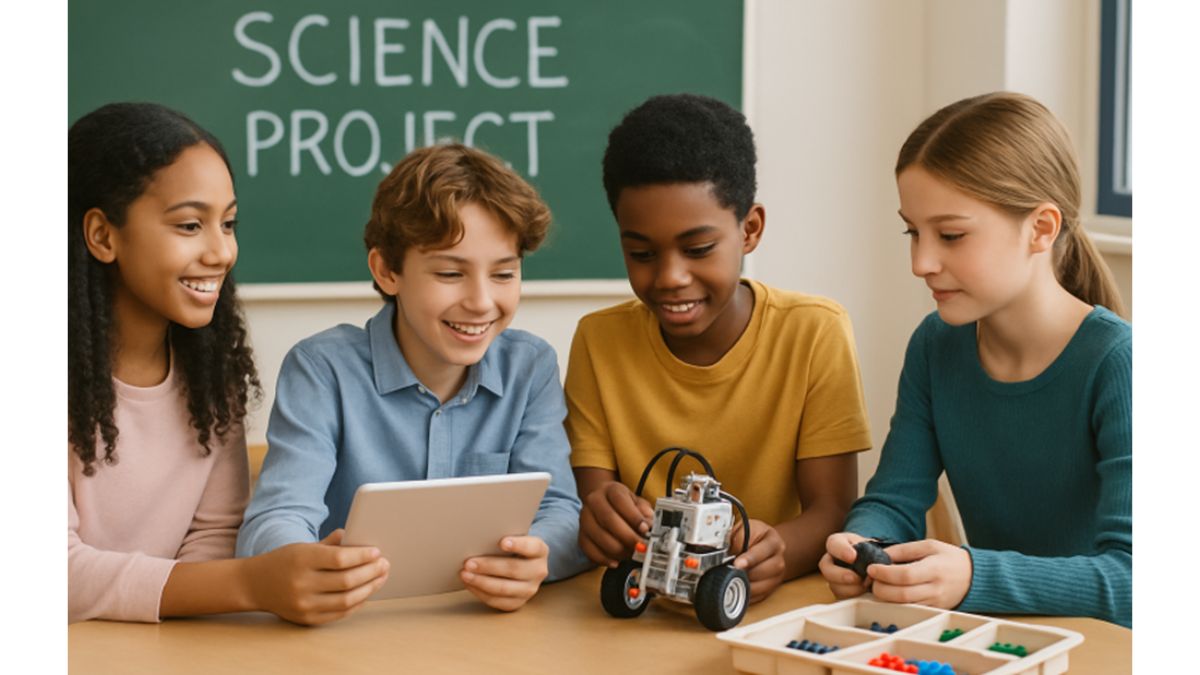
Engaging students in hands-on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) learning during their middle school years is pivotal for nurturing curiosity and sparking a passion for discovery. As education evolves, more schools are embracing an interactive approach, one that makes science and math lively, relevant, and deeply memorable. Institutions, such as the innovative STEM-focused school in Sandy, Utah, are leading the way by making experiential STEM education central to their mission, providing learners with opportunities to solve real-world problems and engage with the broader scientific community.
Hands-on activities encourage critical thinking, creativity, and persistence. These learning methods break complex theories down, making challenging subjects more accessible and engaging. For many students, these early experiences are the gateway to lifelong learning and future STEM careers, as project-based exploration replaces rote memorization and passive classroom routines. When schools invest in dynamic STEM programs, children are better equipped to face the challenges of a rapidly changing technological landscape.
The impact of hands-on activities is supported by research and success stories nationwide. Interactive experiments and student-led projects promote more profound understanding and longer-lasting retention, providing an essential bridge between textbook learning and practical application.
This article explores the importance of hands-on STEM, highlights schools that have excelled in these areas, and provides actionable strategies for educators looking to enhance STEM learning in their classrooms. It also addresses challenges and future trends that will continue shaping middle school STEM education. For more information on educational strategies, visit Edutopia’s STEM resources.
Importance of Hands-On STEM Learning
Active, immersive STEM learning allows students to go beyond theoretical knowledge. When kids design electronics, build robots, or grow plants in a scientific experiment, they master key concepts through trial and error, experimentation, and observation. According to National Geographic Education, tactile learning improves motivation and fosters a sense of ownership over the learning process.
In addition, these activities strengthen problem-solving, communication, and teamwork skills. When middle school classrooms foster an environment of discovery, students feel empowered to ask questions, challenge ideas, and seek solutions. This not only benefits academic growth but also boosts confidence and prepares students for future STEM pursuits.
Successful Initiatives in Middle Schools
Across the United States, creative programs are transforming the way middle school students experience STEM subjects:
- Pickerington Local Schools: Harmon and Diley Middle Schools in Ohio received grants to enhance hands-on STEM learning through student-driven projects, supporting activities that cultivate both technical and creative skills. These grants have helped buy robotics kits, engineering materials, and scientific tools that inspire innovation and hands-on exploration.
- Bath Middle School: In Maine, Bath Middle School launched a STEM+M (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math, and Manufacturing) initiative, introducing students to robotics, engineering challenges, and basic manufacturing processes. The goal is to fill industry gaps and expose students to practical, hands-on skills relevant in today’s workforce.
- UNLV and UNR Extension Workshop: In Nevada, university-led workshops have brought hydroponics and high-tech tools into classrooms, allowing students to experiment with controlled plant growth and digital technologies and to make direct connections between classroom learning and pressing scientific questions.
Strategies for Implementing Hands-On STEM Activities
To create a robust hands-on STEM environment, schools and educators can adopt several strategies:
- Integrate Project-Based Learning: Create real-world challenges for students to solve, utilizing inquiry-driven projects that demand research, experimentation, and collaboration. These projects can tie into community needs, ecology, or other relevant themes.
- Leverage Technology and Robotics: Use coding platforms, circuit kits, and robotics competitions to bring technology to life and make lessons interactive. Gamifying science and math content can help students visualize abstract concepts.
- Build Industry Partnerships: Work with local businesses or universities to give students direct exposure to STEM careers and mentorship opportunities. These relationships allow students to see their classroom knowledge applied beyond school walls and inspire new aspirations.
Overcoming Challenges in STEM Education
Despite clear benefits, hands-on STEM learning faces hurdles, including limited funding, insufficient resources, and gaps in teacher training. Schools can address these obstacles by:
- Pursuiproperants and Support: Tap into external funding providers and local organizations dedicated to enhancing STEM learning, ensuring classrooms have up-to-date materials and access to professional-grade resources.
- Expanding Professional Development: Regular workshops and training for teachers help them become more comfortable with new technologies and teaching approaches, keeping educators at the forefront of their field.
- Promoting Inclusion: Design curricula accessible to students from all backgrounds, with particular attention to underrepresented groups in STEM. Inclusive environments promote equity and inspire traditionally marginalized populations.
Future Trends in Middle School STEM Education
The landscape of STEM education is rapidly changing, with several emerging trends shaping how educators can prepare students for tomorrow’s challenges:
- Personalized Learning through AI: Artificial Intelligence and machine learning platforms offer adaptive feedback and customized lesson adjustments, allowing educators to tailor experiences to each student’s needs while tracking progress and identifying growth opportunities.
- Focus on Environmental Science: Sustainability, climate change, and environmental stewardship are becoming embedded in STEM programs. Engaging students with ecology, renewable energy, and real-world citizen science projects fosters responsibility and global awareness.
- Remote and Hybrid Instruction: Online and hybrid models break down geographical barriers, letting students collaborate on STEM projects, access resources, and interact with experts from anywhere. This flexibility supports both individualized pacing and innovative teamwork.
Hands-on STEM learning is not just about building circuits or running experiments; it’s about cultivating a mindset that values inquiry, resilience, and wonder. With the right support and a focus on innovation, today’s classrooms can prepare the next generation of scientists, engineers, and problem-solvers to thrive in an unpredictable, technological world.