Key Takeaways
- Intraoral scanners provide detailed digital impressions, enhancing workflow accuracy and patient comfort.
- 3D printing streamlines the creation of dental restorations, offering bespoke solutions at unmatched speed.
- Artificial intelligence is setting new standards in diagnostics and personalized treatment planning.
- Teledentistry improves access to care, particularly for underserved and remote populations.
- Augmented reality is reshaping dental education and skills training for the next generation of surgeons.
Table of Contents
Advances in digital technology are reshaping how dental surgical procedures are planned and performed. Tools such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), digital impressions, and 3D imaging allow clinicians to visualize oral structures with greater precision before treatment begins. Computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems also support the creation of accurate surgical guides and restorations, helping streamline workflows while reducing variability during procedures.
Digital education and data-sharing platforms have also become more prominent in modern dental surgery. Virtual simulations, online case reviews, and digitally documented outcomes allow practitioners to refine techniques and stay informed about evolving standards. Institutions such as the Pikos Institute are often cited in discussions of advanced surgical training, reflecting the broader shift toward technology-supported learning. Overall, digital integration continues to influence decision-making, procedural accuracy, and professional development across the field, contributing to more predictable and well-documented surgical outcomes.
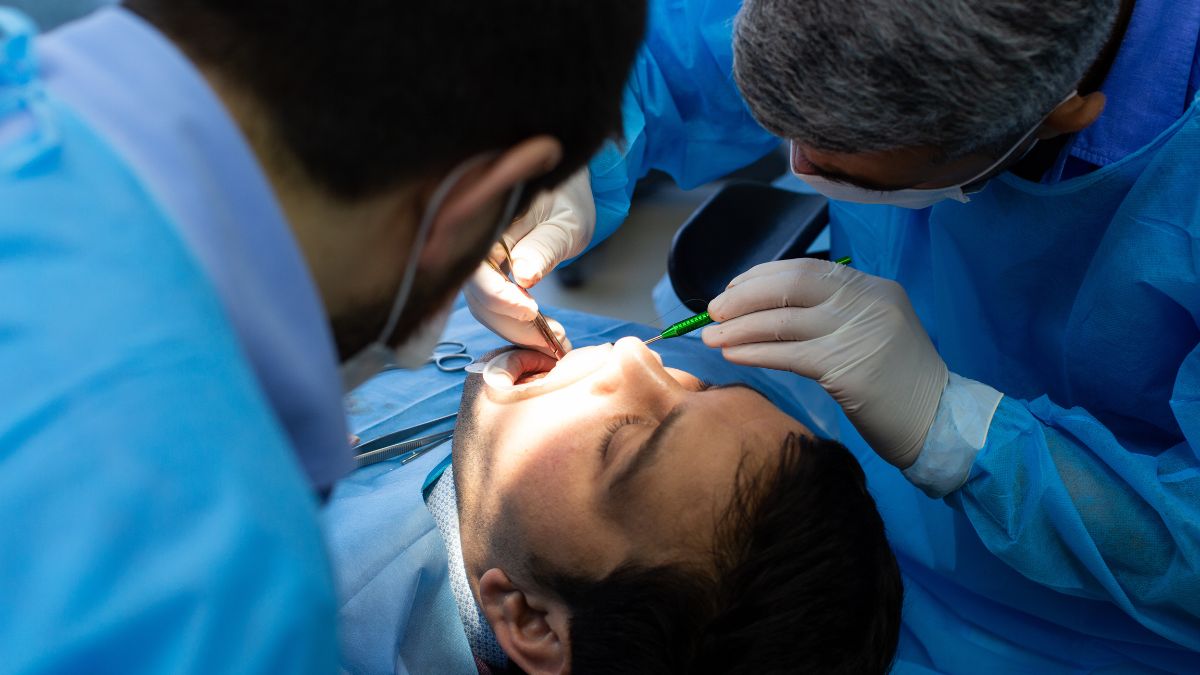
Intraoral Scanners: Enhancing Precision and Comfort
Intraoral scanners (IOS) are changing how dental professionals capture dental impressions. Traditional molds were often uncomfortable for patients and susceptible to human error. With IOS devices, clinicians can quickly create highly detailed digital models, ensuring more precise restorations from the outset. These digital impressions reduce the likelihood of remakes and can be sent to dental labs instantly, decreasing turnaround time and elevating patient comfort. Ongoing advancements are making these scanners increasingly affordable and accessible, leading to widespread adoption across dental practices.
3D Printing: Revolutionizing Dental Prosthetics
3D printing is transforming dental prosthetic production, enabling rapid, on-demand creation of crowns, bridges, dentures, and surgical guides. New resin and ceramic materials give dental restorations improved durability and aesthetics, matching the appearance and strength of natural teeth. By utilizing digital scans, labs can fabricate highly customized prosthetics that perfectly fit each patient. The integration of 3D printing into everyday workflows helps avoid delays, ensures a precise fit, and reduces overall production costs, benefits that are quickly making this technology standard in top practices.
Artificial Intelligence: Transforming Diagnostics and Treatment Planning
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing clinical dentistry by enabling advanced diagnostics and data-driven treatment planning. Machine learning algorithms can interpret radiographs, CBCT scans, and intraoral images faster and more accurately than ever before. This early detection capability leads to better prognoses for common dental diseases like caries and periodontal conditions. AI can also recommend tailored treatment plans by analyzing data from thousands of similar cases, reducing planning time and minimizing risks. As AI-based systems are validated and standardized, they are quickly becoming a crucial part of the dental workflow.
Teledentistry: Expanding Access to Care
Teledentistry is opening new pathways to care by leveraging secure communication platforms for consultations, assessments, and follow-ups. This digital model enables patients in remote, rural, or underserved areas to access quality care and expert advice without frequent travel. Dentists can review photos, radiographs, and patient histories in real time, providing timely support and monitoring for ongoing cases. In addition to addressing barriers related to geography or mobility, teledentistry promotes patient engagement, offers flexible scheduling, and streamlines communication. These benefits are supported by research and policy recommendations from organizations like the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT.
Augmented Reality: Innovating Dental Training
Augmented reality (AR) is bridging the gap between classroom learning and real-world experience in dental education and surgical training. By using AR headsets and simulation platforms, dental students and professionals can practice complex procedures in a controlled, virtual setting, gaining hands-on skills without risk to actual patients. AR also improves communication between practitioners and dental laboratories, facilitates the design of CAD/CAM restorations, and helps guide intraoral scanning. These immersive tools are part of a broader digital movement that supports lifelong learning and increased excellence in dental care.
Conclusion
Digital innovation is steadily redefining modern dental surgery, improving how clinicians diagnose, plan, perform, and learn. From intraoral scanning and 3D printing to AI-driven diagnostics, teledentistry, and augmented reality training, these technologies support greater precision, efficiency, and accessibility across the field. As digital tools continue to mature and integrate into everyday practice, they are helping establish more predictable outcomes, enhanced patient experiences, and a stronger foundation for ongoing professional development in dental surgery.