In today’s connected world, every device—whether a smartphone, laptop, smart TV, or server—relies on unique identifiers to communicate across networks. Two of the most important identifiers are the IP address and the MAC address. While both are essential for networking, they serve very different purposes and operate at different levels of the network architecture. Many users, bloggers, and even beginners in IT often confuse these two concepts or assume they are interchangeable.
This in-depth guide explains the different between IP address and MAC address in a simple, professional, and practical way. You’ll learn how each works, where each is used, why both are necessary, and how understanding them can improve your networking knowledge, troubleshooting skills, and online security awareness. Whether you are a tech enthusiast, student, blogger, or business owner, this article is designed to be clear, trustworthy, and ready for publication.
Table of Contents
Understanding Network Identification Basics
Before comparing the two, it’s important to understand why networks need identifiers at all.
Every network—local or global—needs a way to recognize devices and route data correctly. Without unique identifiers, data packets would never reach the right destination. IP addresses and MAC addresses solve this problem, but at different layers and for different scopes.
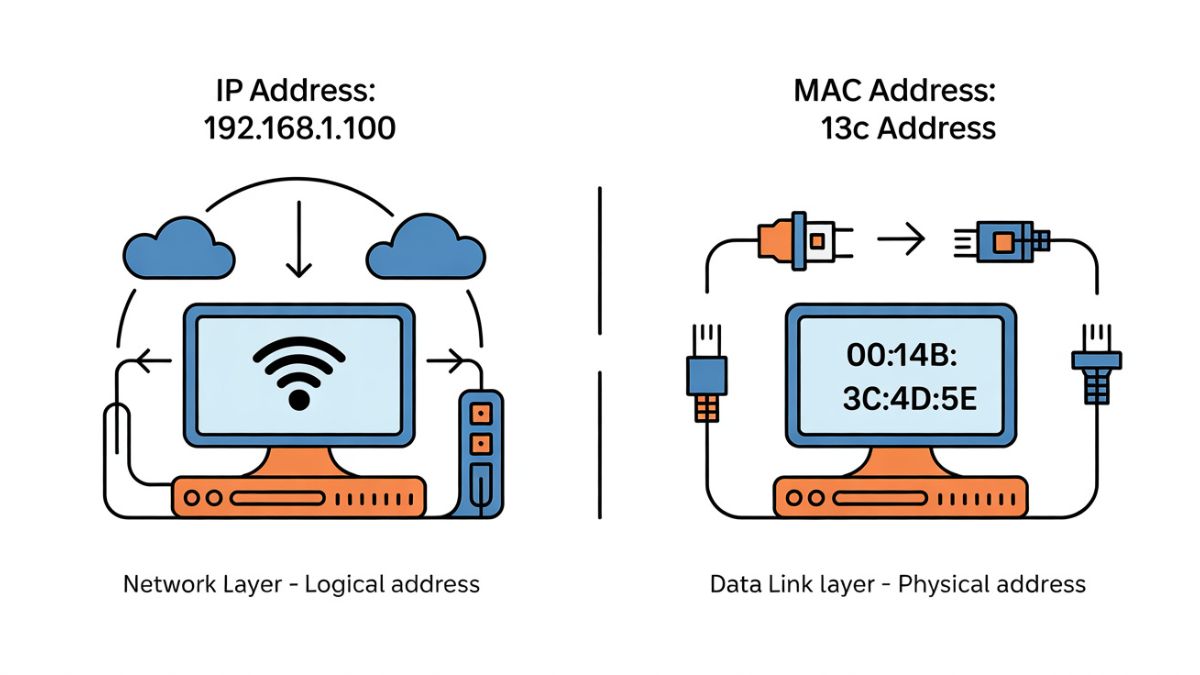
What Is an IP Address?
An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a logical address assigned to a device when it connects to a network. It allows devices to send and receive data over local networks and the internet.
Purpose of an IP Address
The primary role of an IP address is routing. It tells the network where a device is located so data packets can travel from source to destination efficiently. IP addresses can change depending on the network you connect to.
Types of IP Addresses
There are two main versions used today.
IPv4
IPv4 uses a 32-bit address format, written as four numbers separated by dots, such as 192.168.1.1. It is still widely used but has a limited number of unique addresses.
IPv6
IPv6 uses a 128-bit format, written in hexadecimal, such as 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334. It was introduced to solve the address shortage problem and supports a vastly larger number of devices.
What Is a MAC Address?
A MAC address, or Media Access Control address, is a physical, hardware-based identifier assigned to a network interface card by the manufacturer.
Purpose of a MAC Address
The MAC address identifies a device within a local network. It ensures that data sent within a LAN reaches the correct physical device.
Structure of a MAC Address
A MAC address typically looks like this: 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E.
It consists of 12 hexadecimal characters and is usually permanent, although modern systems allow temporary changes for privacy.
Core Different Between IP Address and MAC Address
Understanding the different between IP address and MAC address requires looking at how they function, where they operate, and how they are assigned.
Network Layer vs Hardware Layer
IP addresses operate at the network layer and are managed by software and network protocols. MAC addresses operate at the data link layer and are tied directly to hardware.
Logical vs Physical Identification
An IP address is a logical identifier that can change. A MAC address is a physical identifier embedded in the device’s network interface.
Scope of Use
IP addresses are used for global communication across networks and the internet. MAC addresses are used only within local networks.
IP Address vs MAC Address: Key Differences at a Glance
| Aspect | IP Address | MAC Address |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Logical address | Physical address |
| Assigned By | Network or ISP | Manufacturer |
| Changes Over Time | Yes | Usually no |
| Scope | Global | Local |
| OSI Layer | Network layer | Data link layer |
| Example | 192.168.1.1 | 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E |
This table alone helps clarify the practical different between IP address and MAC address for everyday use.
How IP and MAC Addresses Work Together
Despite their differences, IP and MAC addresses are not competitors—they are partners.
When you send data over a network, your device uses the destination IP address to determine where the data should go. Inside the local network, the Address Resolution Protocol maps that IP address to the correct MAC address. This collaboration ensures accurate and efficient data delivery.
Role in Local Networks
Within a local network, switches rely on MAC addresses to forward data to the correct device. Routers, on the other hand, rely on IP addresses to move data between networks.
This separation of responsibilities is another key different between IP address and MAC address that highlights why both are essential.
Role in Internet Communication
On the internet, IP addresses are critical. They allow routers worldwide to identify networks and direct traffic accordingly. MAC addresses are not transmitted over the internet; they remain local to each network segment.
Security Implications
IP Address Security
IP addresses can reveal approximate location and network details. Firewalls, VPNs, and proxy servers are commonly used to protect and mask IP addresses.
MAC Address Security
MAC addresses can be used for device filtering and access control within networks. However, they can also be spoofed, which is why relying solely on MAC filtering is not recommended for strong security.
Static vs Dynamic Addressing
Static IP Addresses
These remain constant and are often used for servers, websites, and remote access systems.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Assigned automatically by a DHCP server, these change over time and are commonly used for home and mobile devices.
MAC addresses, by default, remain static, reinforcing another important different between IP address and MAC address.
Real-World Examples
Imagine sending an email from your laptop. Your IP address helps route the email across the internet to the recipient’s mail server. Within your home network, your router uses your laptop’s MAC address to ensure the data packets are delivered to your specific device.
Common Myths Explained
Many people believe that MAC addresses can be tracked globally like IP addresses. This is false. MAC addresses do not travel across the internet. Another common myth is that changing an IP address hides your device completely, which is not always true without additional privacy tools.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Knowing the different between IP address and MAC address helps with troubleshooting network issues, improving security configurations, and making informed decisions about privacy and device management. It is also essential knowledge for anyone working with websites, servers, or digital infrastructure.
Conclusion
Understanding the different between IP address and MAC address is fundamental to grasping how modern networks operate. IP addresses act as dynamic, logical identifiers that guide data across the internet, while MAC addresses serve as fixed, physical identifiers within local networks. Each plays a distinct yet complementary role in ensuring reliable, efficient, and secure communication between devices.
By clearly distinguishing their purposes, functions, and limitations, you gain better control over networking decisions, security practices, and troubleshooting strategies. Whether you’re managing a website, learning networking basics, or simply curious about how the internet works behind the scenes, mastering this distinction empowers you with knowledge that is both practical and essential in today’s digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main different between IP address and MAC address?
The main difference is that an IP address is a logical, changeable identifier used for routing across networks, while a MAC address is a physical, hardware-based identifier used within local networks.
Can two devices have the same IP address?
Yes, on different networks, devices can share the same IP address. However, within the same network, IP addresses must be unique to avoid conflicts.
Can a MAC address be changed?
Technically, yes. Many operating systems allow MAC address spoofing for privacy or testing, but the original hardware address remains unchanged internally.
Which is more important for internet access?
IP addresses are essential for internet access. MAC addresses are important only within local networks and do not function globally.
Is an IP address more secure than a MAC address?
Neither is inherently more secure. Security depends on how they are managed, protected, and combined with other tools like firewalls and encryption.
Do VPNs hide MAC addresses?
VPNs hide your IP address from external networks, but they do not hide your MAC address from your local network.